Knee Arthritis
Knee Arthritis: A Degenerative Joint Condition That May Impact Mobility and Daily Activities
Knee arthritis is a common condition where the cartilage that cushions the knee joint gradually wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This degenerative condition can significantly impact daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or standing for extended periods. While most common in older adults, knee arthritis can also affect younger individuals, especially those with previous knee injuries or certain medical conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee arthritis is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life.
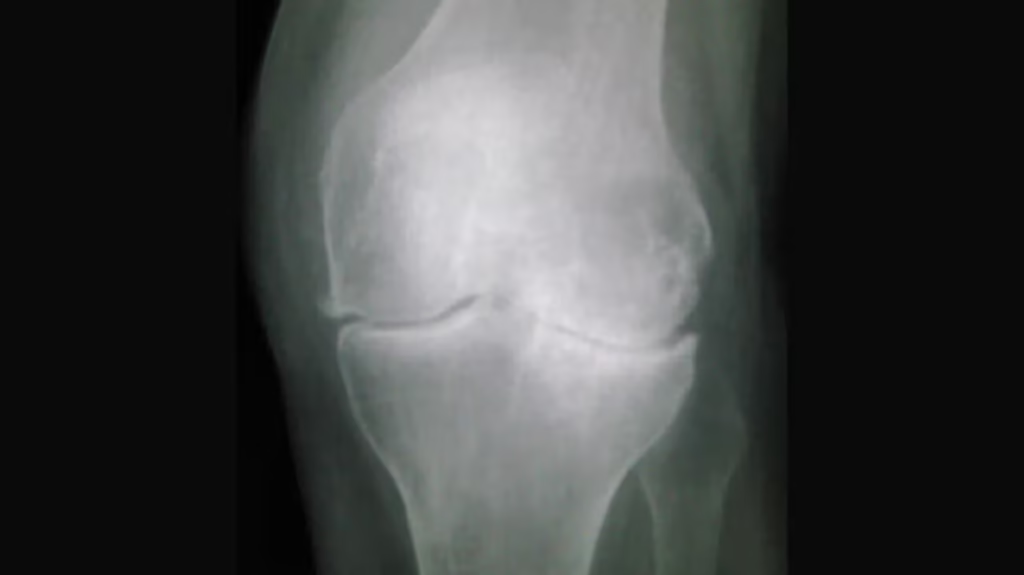
What Is Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee joint breaks down over time. This can lead to bones rubbing against each other, causing pain, swelling, and inflammation.
There are different types of arthritis that can affect the knee, including:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common type, caused by wear and tear over time.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joint lining.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops after a knee injury, such as a fracture or ligament tear.
Causes Of Knee Arthritis
The exact cause of knee arthritis depends on the type, but contributing factors may include:
- Ageing: Natural wear and tear on the joint over time.
- Injury: Previous injuries, such as fractures, ligament tears, or meniscal damage.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation from autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Genetics: Family history of arthritis may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Symptoms Of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis symptoms can vary in severity but often include:
- Pain, especially during activity or after prolonged sitting.
- Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after inactivity.
- Swelling around the knee joint.
- Reduced range of motion, making it difficult to bend or straighten the knee.
- A feeling of instability or the knee “giving way.”
- Grinding or clicking sounds during movement.
If you experience these symptoms, consulting a medical professional may help determine the cause and explore treatment options.
Risk Factors For Knee Arthritis
Several factors may increase the risk of developing knee arthritis, including:
- Age: The risk increases with age due to natural joint wear.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure to the knee joint, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
- Injuries: Previous knee injuries, such as ACL tears or fractures, can increase the risk.
- Repetitive Stress: Jobs or activities that place repeated strain on the knee joint.
- Genetics: Family history of arthritis can increase susceptibility.
Treatment Options For Knee Arthritis
Treatment for knee arthritis focuses on relieving symptoms, improving mobility, and slowing progression. Options may include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, regular low-impact exercise, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Physiotherapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee and improve joint function.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications or pain relievers may help manage symptoms.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical treatments are no longer effective, surgical options may be considered, such as:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure to remove loose cartilage or damaged tissue.
- Osteotomy: A knee realignment procedure to shift weight away from the damaged area.
- Knee Replacement: Partial or total knee replacement may be recommended for advanced arthritis.
The best treatment option depends on the severity of the arthritis, the patient’s overall health, and their activity goals.
When Should You Seek Help For Knee Arthritis?
You should consider seeking medical advice if:
- Pain or stiffness limits your daily activities or quality of life.
- Symptoms persist despite trying over-the-counter treatments.
- You experience swelling, redness, or instability in the knee.
Early diagnosis and intervention may help slow the progression of arthritis and improve outcomes.
If you would like to learn more about knee arthritis or discuss your options, book an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group.
