A Painful Or Failing Knee Replacement
A Painful or Failing Knee Replacement: Complications That May Affect Function and Quality of Life
While knee replacement surgery is often successful in reducing pain and improving mobility for individuals with advanced knee arthritis or joint damage, some patients may experience complications or ongoing discomfort after the procedure. A painful or failed knee replacement refers to cases where the surgery does not achieve the expected outcomes, leading to persistent pain, stiffness, or instability. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment to restore function and improve quality of life.
- What Is A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement?
- Causes Of A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
- Symptoms Of A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
- Risk Factors For Complications After Knee Replacement
- Treatment Options For A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
- When Should You Seek Help For A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement?
What Is A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement?
A painful or failed knee replacement occurs when the results of a total or partial knee replacement surgery are not satisfactory. This may involve ongoing pain, stiffness, instability, or a failure of the implant to function as intended.
In some cases, the implant may loosen, wear out, or become misaligned, leading to mechanical issues. In others, complications such as infection or scar tissue formation may contribute to pain and impaired function.
Causes Of A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
Several factors can contribute to a painful or failed knee replacement, including:
- Infection: A post-surgical infection in the knee joint can cause pain, swelling, and instability.
- Implant Loosening: Over time, the implant may become loose due to wear and tear or improper fixation.
- Malalignment: Misalignment of the implant can affect joint function and lead to discomfort.
- Scar Tissue Formation: Excessive scar tissue around the knee joint may restrict movement and cause stiffness.
- Wear of the Implant: The artificial components of the knee replacement can wear down over time, especially in active individuals.
- Fracture or Bone Loss: Bone fractures or significant bone loss near the implant may compromise its stability.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions such as inflammatory arthritis or nerve-related pain may contribute to ongoing symptoms.
Symptoms Of A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
Symptoms of a painful or failed knee replacement may include:
- Persistent or worsening pain in the knee joint.
- Swelling or redness around the knee.
- Stiffness or limited range of motion.
- A feeling of instability or the knee “giving way.”
- Clicking, grinding, or other unusual noises during movement.
- Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily activities.
If these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
Risk Factors For Complications After Knee Replacement
Certain factors may increase the risk of complications or failure after knee replacement surgery, including:
- Age: Younger, more active patients may place greater stress on the implant, leading to wear or loosening.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, or osteoporosis may affect healing and implant longevity.
- Infection History: A history of joint infections can increase the risk of post-surgical complications.
- High-Impact Activities: Engaging in activities that place excessive stress on the knee joint may accelerate implant wear.
- Surgical Technique: Improper alignment or fixation of the implant during surgery.
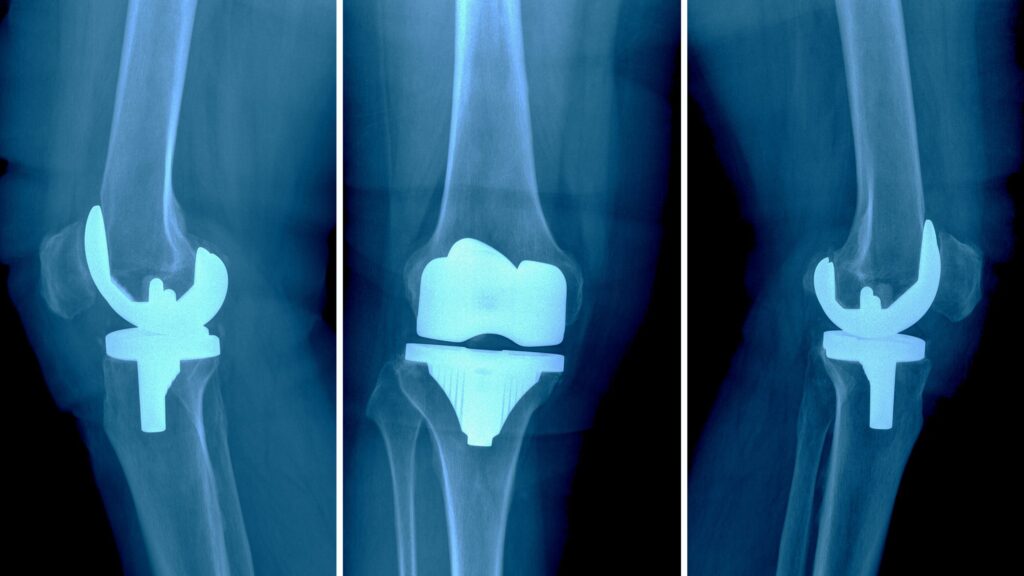
Treatment Options For A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement
Treatment for a painful or failed knee replacement depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Options may include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Pain Management: Medications or injections to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises to improve knee function and reduce stiffness.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding high-impact activities that may exacerbate symptoms.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be recommended if non-surgical treatments are ineffective or if mechanical issues are identified:
- Revision Knee Replacement Surgery: Replacing or adjusting the original implant to address loosening, wear, or misalignment.
- Infection Management: Removing infected tissue and replacing the implant, if necessary.
- Bone Grafting: Using bone grafts to restore bone loss around the implant.
Dr. Scott Tulloch will perform a comprehensive assessment to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific condition.
When Should You Seek Help For A Painful Or Failed Knee Replacement?
You should consider seeking medical advice if:
- You experience persistent pain, swelling, or stiffness after knee replacement surgery.
- You notice instability, unusual noises, or difficulty with knee movement.
- You have signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or fever.
Early evaluation and intervention may help identify the cause of your symptoms and improve your overall outcome.
If you would like to learn more about painful or failed knee replacements or discuss your treatment options, book an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group.
