HIP BURSITIS/GLUTEAL TEAR & TENDIOPATHY
Hip Bursitis / Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy: Inflammation and injury affecting the hip's soft tissues
Hip bursitis, gluteal tears, and gluteal tendinopathy are conditions that affect the soft tissues surrounding the hip joint. These conditions cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, impacting daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing for extended periods.
Hip bursitis occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint, become inflamed or irritated.
Gluteal tears happen when the tendons of the gluteal muscles (particularly the gluteus medius or gluteus minimus) partially or fully tear, affecting hip stability and strength.
Gluteal tendinopathy refers to chronic damage, thickening, or degeneration of the gluteal tendons, often due to overuse or repetitive strain.
These conditions can develop gradually or occur suddenly due to injury. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce pain, restore function, and prevent further damage.
- Causes Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
- Symptoms Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
- Risk Factors For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
- Diagnosis Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
- Treatment Options For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
- When Should You Seek Help For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy?
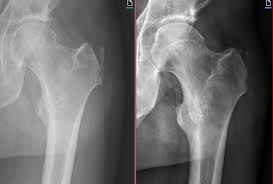
Causes Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
These conditions can result from a variety of causes, including:
- Repetitive Movements and Overuse: Repetitive activities like running, walking, or stair climbing can cause strain on the hip tendons and bursae, leading to irritation or small tears.
- Trauma or Injury: A sudden fall or direct impact to the hip can cause bursitis or a tear in the gluteal tendons. This type of injury is common in athletes and people who participate in high-impact sports.
- Muscle Imbalance or Weakness: Weakness in the hip muscles can cause an imbalance in how the joint is loaded, leading to excessive strain on the tendons or bursae.
- Prolonged Pressure on the Hip: Activities like sitting or lying on one side for extended periods can place excessive pressure on the bursae, leading to bursitis.
- Tendon Degeneration: Gluteal tendinopathy can develop as a result of age-related wear and tear on the tendons, leading to thickening, scarring, and reduced tendon elasticity.
- Poor Biomechanics: Abnormal walking patterns, flat feet, or misalignment of the hip, knee, or ankle joints can place additional stress on the tendons and bursae, increasing the risk of injury.
Symptoms Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
The symptoms of hip bursitis, gluteal tears, and tendinopathy may vary depending on the specific condition and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain on the Outer Side of the Hip: Pain is typically felt on the side of the hip (greater trochanter) and may worsen when lying on the affected side.
- Pain with Movement: Activities like walking, climbing stairs, running, or standing for extended periods may worsen the pain.
- Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion: Pain and inflammation can limit your ability to rotate, bend, or move the hip freely.
- Pain When Lying on the Affected Side: Many people with hip bursitis or gluteal tears report discomfort when sleeping or resting on the affected hip.
- Hip Weakness: Damage to the gluteal tendons may lead to weakness in the hip muscles, affecting stability and balance.
- Swelling and Tenderness: The area around the hip may feel swollen, warm, or tender to the touch, especially in cases of bursitis.
If you experience any of these symptoms, particularly if they persist or worsen, you may benefit from seeking medical advice to prevent further joint or tendon damage.
Risk Factors For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
Some factors that increase the likelihood of developing these conditions include:
- Age: Tendon degeneration increases with age, making older adults more prone to gluteal tendinopathy and tendon tears.
- Female Gender: Women are more likely to develop gluteal tendinopathy due to differences in pelvic structure, which can increase stress on the hip tendons.
- Overuse and Repetitive Activities: High-impact sports like running, cycling, or hiking place repeated strain on the hip tendons and bursae.
- Muscle Weakness or Imbalance: Weakness in the hip, gluteal, or core muscles can increase the load on the gluteal tendons and bursae, leading to overuse injuries.
- Occupation and Lifestyle Factors: Jobs or hobbies that require prolonged standing, walking, or stair climbing can place excess strain on the hip joint.
- Poor Biomechanics: Issues like leg length differences, flat feet, or misaligned hip joints can create uneven pressure on the tendons and bursae, increasing the risk of injury.
- Prior Hip Injury: People with a history of hip dislocations, fractures, or past injuries may be more susceptible to gluteal tears or hip bursitis.
Being aware of these risk factors can help you take proactive measures to reduce your risk of developing these conditions.
Diagnosis Of Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate treatment. Dr Scott Tulloch may use the following steps to assess your condition:
- Clinical Examination: Dr Tulloch will discuss your symptoms, review your medical history, and perform a physical assessment. He may apply pressure to the hip to identify areas of tenderness or swelling.
- Range of Motion and Strength Testing: Specific movements or resistance tests may be used to identify tendon weakness, pain, or reduced range of motion.
Imaging Tests:
- X-Rays: X-rays can help rule out other causes of hip pain, such as fractures or arthritis.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, tendons, and bursae. It can reveal inflammation, tendon tears, or degeneration.
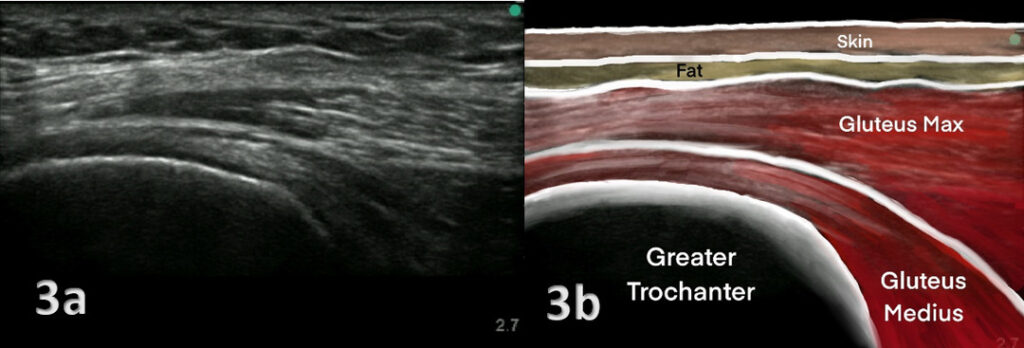
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan can be used to detect bursitis or damage to the gluteal tendons.
After diagnosis, Dr. Tulloch will develop a personalised treatment plan tailored to your needs and lifestyle.
Treatment Options For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy
Treatment options for hip bursitis, gluteal tears, and tendinopathy depend on the severity of the condition. Both non-surgical and surgical options may be considered.
Non-Surgical Treatment
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing activities that strain the hip joint may allow the injury to heal naturally.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapy program can help improve hip strength, stability, and range of motion. Strengthening the gluteal muscles may reduce strain on the tendons and bursae.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications may relieve pain and swelling.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain, particularly for hip bursitis.
Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be required. Options include:
- Gluteal Tendon Repair: If the gluteal tendon is torn, surgery may be required to reattach the tendon to the bone.
- Bursal Removal (Bursectomy): In cases of chronic bursitis, the inflamed bursa may be removed.
- Tendon Release: This involves releasing tight or damaged tendons to reduce pressure on the hip joint.
Your treatment plan will be based on your symptoms, lifestyle, and the severity of your condition.
When Should You Seek Help For Hip Bursitis, Gluteal Tear & Tendinopathy?
If hip pain, stiffness, or limited movement is affecting your ability to walk, work, or sleep, you should seek medical advice. Early intervention can prevent further damage to the tendons and bursae.
If you would like to learn more about treatment options for hip bursitis, gluteal tears, or tendinopathy, contact the Victorian Orthopaedic Group to schedule an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch.
