A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
A Painful or Failing Hip Replacement: When an artificial joint no longer functions as intended
A painful or failing hip replacement occurs when an artificial hip joint no longer functions as intended, leading to discomfort, instability, or loss of mobility. This situation can arise for several reasons, such as implant wear and tear, loosening, infection, or fractures around the implant. While hip replacements are designed to last for many years, complications may develop over time, requiring medical intervention or revision surgery to restore comfort and mobility.
Early diagnosis and treatment of a failing hip replacement are essential to avoid further damage to the hip joint, reduce pain, and maintain quality of life.
- What Causes A Hip Replacement To Fail?
- Symptoms Of A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
- Risk Factors For A Failing Hip Replacement
- Diagnosis Of A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
- Treatment Options For A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
- When Should You Seek Help For A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement?
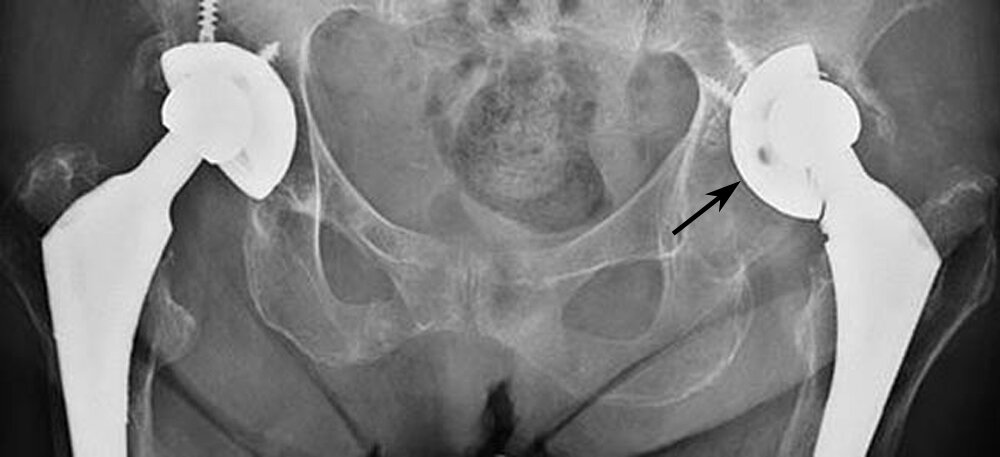
What Causes A Hip Replacement To Fail?
There are several reasons why a hip replacement may fail. Identifying the cause is essential for determining the best course of treatment.
- Implant Wear and Tear: Over time, the materials used in hip replacements (such as metal, ceramic, or plastic) can wear down. Daily movement and activity put pressure on the implant, causing gradual wear. When the bearing surfaces wear out, it may lead to joint instability, pain, and loss of function.
- Loosening of Components: Loosening occurs when the implant separates from the bone or the surrounding cement. This can result from natural bone loss, the body’s reaction to the implant, or improper placement of the prosthetic. Loose components can cause pain, instability, and reduced range of motion.
- Implant Malposition: Accurate positioning of the implant is crucial to the success of a hip replacement. If the components are misaligned or incorrectly positioned, it can lead to abnormal wear, joint instability, and an increased risk of dislocation.
- Dislocation: If the ball of the prosthetic hip pops out of the socket, it results in a dislocated hip. This is more likely to occur if the implant components are not aligned correctly or if the surrounding soft tissues are too weak to stabilise the joint.
- Infection: Infection can occur during surgery or later as a result of an open wound or bloodstream infection. Infections can cause swelling, pain, and implant failure. In some cases, removal of the infected implant is necessary.
- Bone Fracture Around the Implant: Fractures near the site of the hip implant can destabilise the joint. Fractures may result from trauma, like a fall or accident, or from weakened bones due to osteoporosis.
- Implant Fracture: Although rare, implant components can fracture under repeated stress. This type of failure requires surgical intervention to remove and replace the damaged part.
- Metal-on-Metal Reactions: Metal-on-metal implants, which use metal surfaces on both the ball and socket, can release metal ions into the bloodstream, causing inflammation, soft tissue damage, and metallosis (metal toxicity). This may require revision surgery to remove and replace the implant.
Symptoms Of A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
The symptoms of a failing hip replacement can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common signs to look out for include:
- Persistent Hip Pain: Pain may be felt in the groin, thigh, or buttock. It may be constant or increase with movement or weight-bearing activities.
- Instability or feeling of “Giving Way”: A loose or misaligned implant can make the hip feel unstable or like it might give way.
- Reduced Range of Motion: If the implant components are worn, loose, or misaligned, you may have difficulty moving the hip joint fully.
- Clicking, Popping, or Grinding Sensation: You may feel or hear unusual sounds when moving your hip, which can signal a mechanical issue with the implant.
- Limping or Changes in Gait: You may develop a limp or experience difficulty walking as a result of pain, instability, or reduced range of motion.
- Swelling or Warmth Around the Joint: These symptoms may indicate infection or inflammation in the tissues around the implant.
- Leg Length Discrepancy: If the implant loosens or dislocates, one leg may appear shorter than the other.
- Fever or Chills: These may be signs of infection, particularly if accompanied by swelling, pain, or warmth in the hip area.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce the need for more complex revision surgery.
Risk Factors For A Failing Hip Replacement
Certain factors increase the likelihood of hip replacement failure, including:
- Age and Activity Level: Younger, more active people place greater stress on the implant, increasing the risk of wear and tear.
- Obesity: Carrying extra weight places additional strain on the hip joint and implant, potentially accelerating wear.
- Previous Hip Surgery: People with previous hip surgeries may be at increased risk of implant loosening or dislocation.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes can weaken bone strength and increase the risk of implant-related fractures.
- Poor Bone Quality: People with reduced bone density (osteoporosis) are at greater risk of fractures around the implant site.
- Smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow and bone healing, affecting the success of a hip replacement.
- Infection Risk: Poor wound care, existing infections, or immune-compromising conditions may increase the risk of infection around the hip joint.
Diagnosis Of A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
Dr. Scott Tulloch will use a range of diagnostic methods to determine why your hip replacement is failing. These include:
- Clinical Assessment: Dr. Tulloch will review your medical history and perform a physical examination to assess your range of motion, pain levels, and signs of instability or infection.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Used to identify loosening, fractures, malalignment, or component wear.
- MRI or CT scan: Provides detailed images of soft tissue, bones, and the position of the implant components.
- Ultrasound: Used to detect fluid accumulation, swelling, or inflammation.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may identify markers of infection or inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Joint Aspiration (Arthrocentesis): A sample of fluid from the joint may be collected and tested for infection.
Treatment Options For A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement
Treatment for a painful or failing hip replacement depends on the underlying cause. Options include non-surgical and surgical approaches.
Non-Surgical Treatment
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) may help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Infection Management: Infections may be treated with antibiotics. If the infection is severe, the implant may need to be removed.
Surgical Treatment
- Revision Hip Replacement: If the implant is loose, misaligned, worn out, or fractured, a revision hip replacement may be required. This involves removing the old components and replacing them with new ones.
- Treatment of Infection: For severe infections, the infected implant is removed, and the joint is cleaned. In some cases, a two-stage revision may be necessary, where the new implant is inserted after the infection has been cleared.
- Bone Grafting: If bone loss has occurred, a bone graft may be used to strengthen and rebuild the hip joint.
Dr. Tulloch will discuss your treatment options with you and recommend a plan based on your condition and lifestyle.
When Should You Seek Help For A Painful Or Failing Hip Replacement?
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention promptly:
- Severe or worsening hip pain
- Instability or difficulty walking
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the hip
- Fever or signs of infection
Prompt treatment can help reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further damage to the joint.
If you would like to learn more about treatment options for a painful or failing hip replacement, contact the Victorian Orthopaedic Group to schedule an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch.
