Cartilage-related Knee Conditions
Cartilage-Related Knee Conditions: Damage That May Affect Joint Cushioning and Mobility
Cartilage-related conditions in the knee can significantly affect joint function and overall mobility. Cartilage is a smooth, flexible tissue that covers the ends of bones within the knee joint, helping to absorb shock and facilitate smooth movement. Damage to the cartilage, whether from injury, overuse, or degeneration, can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced knee function. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for cartilage-related conditions may help individuals manage their symptoms and preserve knee health.
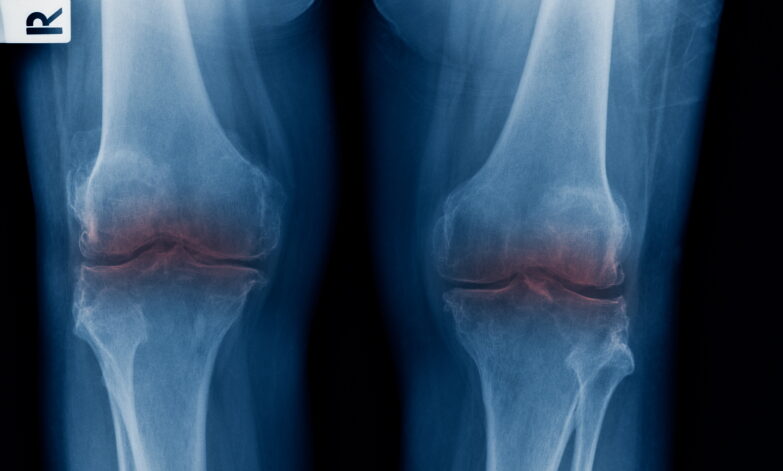
What Are Cartilage-related Conditions?
Cartilage-related conditions in the knee occur when the cartilage is damaged or deteriorates. Common conditions include:
- Chondromalacia Patellae: Softening or breakdown of cartilage on the underside of the kneecap, often resulting in pain during activities such as climbing stairs or running.
- Osteochondritis Dissecans: A condition where a small segment of bone and cartilage separates from the surrounding area, leading to pain and potential joint instability.
- Cartilage Tears: Damage to the cartilage due to injury or trauma, often associated with meniscal tears or ligament injuries.
- Cartilage Degeneration: Gradual wear and tear of the cartilage, commonly linked to ageing or osteoarthritis.
Causes Of Cartilage-related Conditions
Cartilage damage can occur due to:
- Trauma: Direct impact to the knee, such as during sports or falls.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the knee joint from activities like running or jumping.
- Degenerative Changes: Age-related wear and tear leading to cartilage thinning or breakdown.
- Underlying Conditions: Medical conditions such as osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis.
- Congenital Factors: Abnormal joint alignment or genetic predisposition to cartilage weakness.
Symptoms Of Cartilage Damage
Symptoms of cartilage-related conditions can vary but may include:
- Pain in the knee joint, especially during activity or after prolonged sitting.
- Swelling or inflammation around the knee.
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion.
- Grinding, clicking, or popping sensations in the knee.
- A feeling of instability or the knee “giving way.”
If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical advice may help identify the underlying cause and determine appropriate treatment options.
Risk Factors For Cartilage-related Conditions
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing cartilage-related conditions, including:
- Age: Cartilage becomes less resilient with age, increasing the risk of degeneration.
- Sports Participation: High-impact sports such as football, basketball, or skiing can place stress on the knee joint.
- Previous Knee Injuries: A history of knee injuries, such as ligament tears or fractures, may predispose individuals to cartilage damage.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure to the knee joint, accelerating cartilage wear.
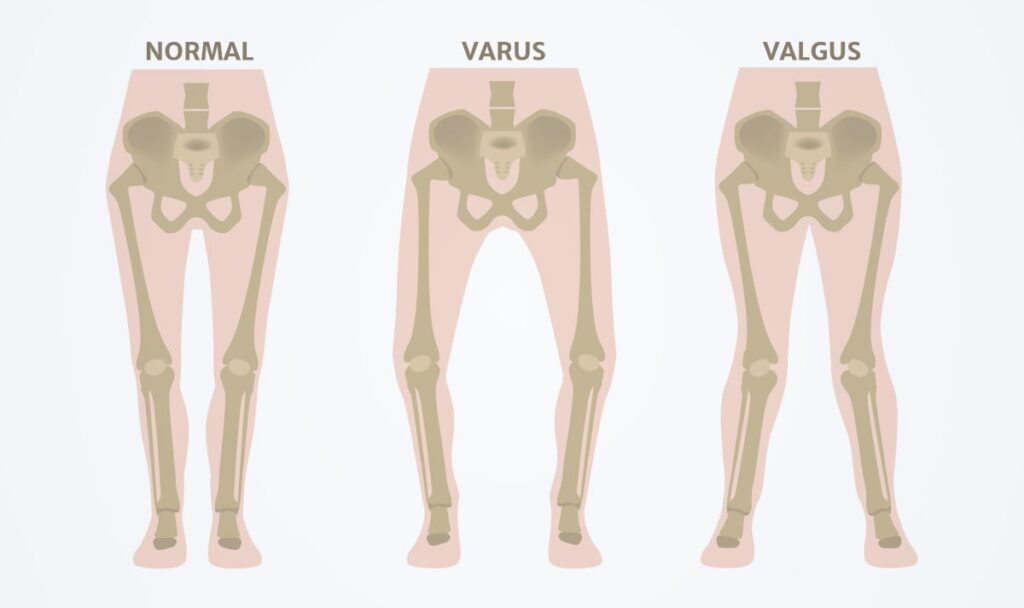
- Joint Malalignment: Conditions such as knock-knees or bow-legs can unevenly distribute weight across the knee, increasing wear on cartilage.
Treatment Options For Cartilage-related Conditions
Treatment for cartilage-related conditions aims to relieve symptoms, improve knee function, and preserve joint health. Options include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms to allow the knee to heal.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening exercises to support the knee joint and improve mobility.
- Medications: Pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications may help manage symptoms.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be recommended for severe or persistent cases of cartilage damage:
- Arthroscopic Debridement: Removing loose fragments of cartilage or smoothing rough edges.
- Cartilage Repair or Restoration: Techniques such as microfracture, osteochondral grafting, or autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI) may help regenerate cartilage.
- Knee Realignment Surgery: Correcting joint malalignment to reduce stress on the cartilage.
- Knee Replacement Surgery: In advanced cases, partial or total knee replacement may be necessary.
Dr. Scott Tulloch will assess your condition and discuss the most appropriate treatment options based on your specific needs and activity goals.
When Should You Seek Help For Cartilage-related Conditions?
You should consider seeking medical advice if:
- Knee pain or stiffness affects your ability to perform daily activities.
- You experience swelling, grinding, or instability in the knee.
- Symptoms persist despite rest, physiotherapy, or other non-surgical treatments.
If you would like to learn more about cartilage-related conditions or discuss your options, book an appointment with Dr. Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group as early intervention may help preserve cartilage health and improve long-term outcomes.
