Hip Arthritis
Hip Arthritis: A Progressive Joint Condition That Can Affect Mobility and Quality of Life
Hip arthritis is a condition where the protective cartilage in the hip joint wears down over time. This degenerative joint condition most often affects older adults but can impact people of all ages. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones of the hip joint begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Hip arthritis can significantly affect daily activities like walking, standing, or climbing stairs, impacting overall quality of life.
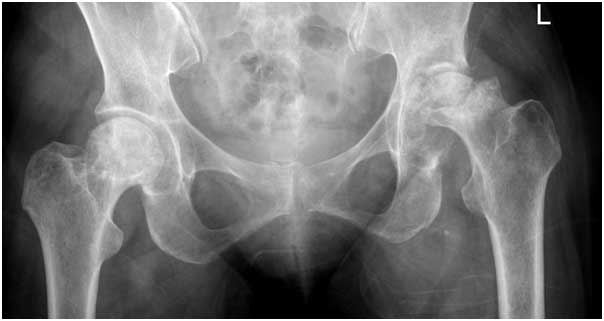
Causes Of Hip Arthritis
Hip arthritis can develop from several underlying causes, including:
- Osteoarthritis: This is the most common cause of hip arthritis. It occurs as a result of natural wear and tear on the hip joint, often linked to ageing. Over time, the cartilage cushioning the joint wears away, leading to pain, stiffness, and loss of function. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and joint strain can contribute to its progression.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This autoimmune condition causes the immune system to attack the synovial lining of the hip joint, leading to inflammation, pain, and joint deformity. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis is an immune-related condition that can affect multiple joints throughout the body.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: A past injury to the hip, such as a fracture or dislocation, can disrupt normal joint function and lead to post-traumatic arthritis. Over time, these disruptions can cause the joint to wear out faster, increasing the likelihood of arthritis.
- Avascular Necrosis (Osteonecrosis): Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to the bone in the hip joint is reduced or cut off. Without adequate blood flow, the bone can weaken or collapse, leading to hip joint damage and, eventually, arthritis. This condition can be linked to trauma, steroid use, excessive alcohol consumption, or certain medical conditions.
Symptoms Of Hip Arthritis
The symptoms of hip arthritis can vary from mild to severe and often develop gradually. Common symptoms may include:
- Hip Pain: Pain is typically felt in the groin, buttocks, or thigh and may worsen with activity.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may also radiate down to the knee, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact source.
- Stiffness: Many people experience stiffness, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Loss of cartilage can limit the movement of the hip joint, making it harder to walk, climb stairs, or sit comfortably.
- Swelling and Inflammation: The joint may become inflamed, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Joint Instability: As the cartilage wears down, the hip joint may feel unstable or as though it might “give way.”
- Grating or Clicking Sensation: Some people describe a “grating” or “crunching” sound when moving the hip.
- Muscle Weakness: Pain and inflammation may cause weakness in the hip muscles, making it difficult to support your body weight.
- Limping or Gait Changes: To compensate for pain and stiffness, some people develop a limp or an altered walking pattern.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to seek medical advice. Early intervention may help slow the progression of arthritis and improve your overall function.
Risk Factors For Hip Arthritis
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing hip arthritis, including:
- Age: The likelihood of hip arthritis increases as we age due to natural wear and tear on the joint.
- Genetics: Family history of hip arthritis can increase your risk, as genetics play a role in joint structure and cartilage health.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop hip arthritis than men, potentially due to hormonal differences and anatomical structure.
- Previous Joint Injuries: A history of hip injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can accelerate joint wear and tear, increasing the risk of post-traumatic arthritis.
- Joint Abnormalities: Conditions such as hip dysplasia (misalignment of the hip joint) can place extra stress on the joint, leading to arthritis over time.
- Excess Body Weight: Carrying extra weight increases pressure on the hip joint, accelerating wear and tear.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis cause chronic joint inflammation, which can lead to arthritis in the hip.
- Avascular Necrosis: Reduced blood flow to the hip joint can weaken the bone and contribute to the development of arthritis.
- Lifestyle and Occupation: Jobs or activities that place repetitive strain on the hip joint may increase the risk of arthritis.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased inflammation and reduced blood flow, both of which may contribute to hip joint deterioration.
Understanding these risk factors can help you identify early signs of hip arthritis and take steps to protect joint health.
Treatment Options For Hip Arthritis
Treatment for hip arthritis aims to manage pain, improve joint function, and maintain quality of life. Treatment plans are personalised based on the severity of your condition and your personal goals. Options may include:
NON SURGICAL TREATMENT
Reducing activities that place stress on the hip, maintaining a healthy weight, and using walking aids, like canes, may help reduce pain.
A personalised physiotherapy program can strengthen the muscles around the hip, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint function.
Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may help manage discomfort. For more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections may provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation or lubricating the joint.
If non-surgical treatments are no longer effective, surgical intervention may be considered. Options include:
SURGICAL TREATMENTS
This minimally invasive procedure allows surgeons to repair or clean out the joint. It is sometimes used to delay the progression of arthritis.
For advanced arthritis, a hip replacement may be recommended. This procedure involves replacing the damaged parts of the joint with a prosthetic implant, allowing for improved mobility and reduced pain.
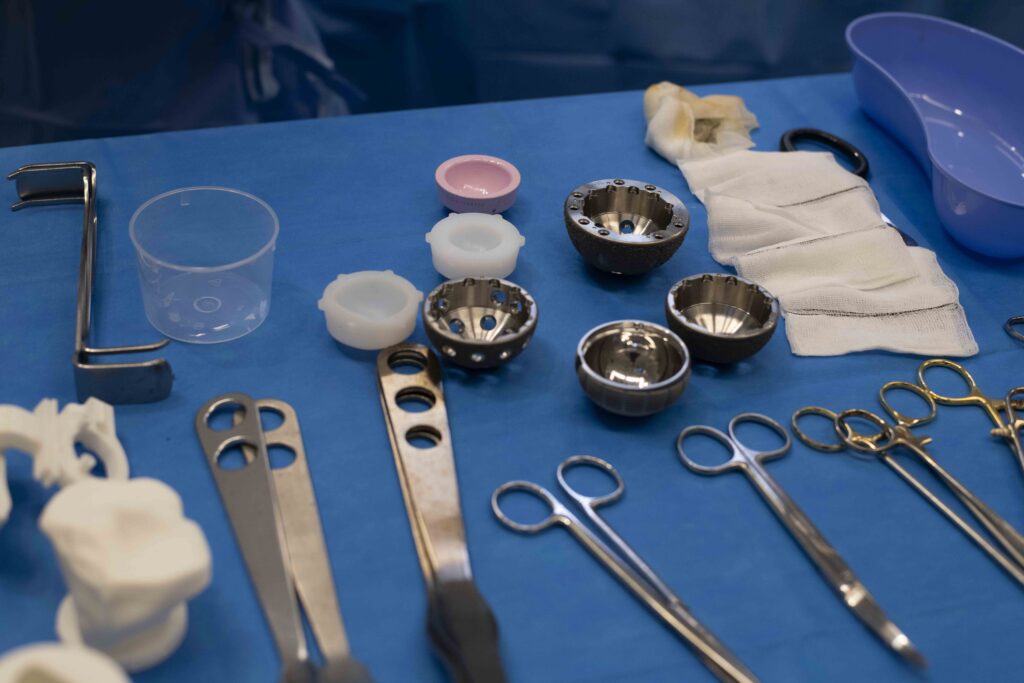
Your treatment plan will depend on your individual condition, lifestyle, and goals. Dr. Scott Tulloch will discuss your options and provide personalised recommendations.
When Should You Seek Help For Hip Arthritis?
If hip pain, stiffness, or limited mobility is affecting your ability to work, exercise, or enjoy daily activities, it may be time to seek professional advice. Early assessment can help identify the stage of arthritis and determine the most appropriate treatment options for you.
If you’d like to learn more or discuss your options, book an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group.
