Knee Fractures
Knee Fractures: Bone Injuries That May Impact Joint Stability and Mobility
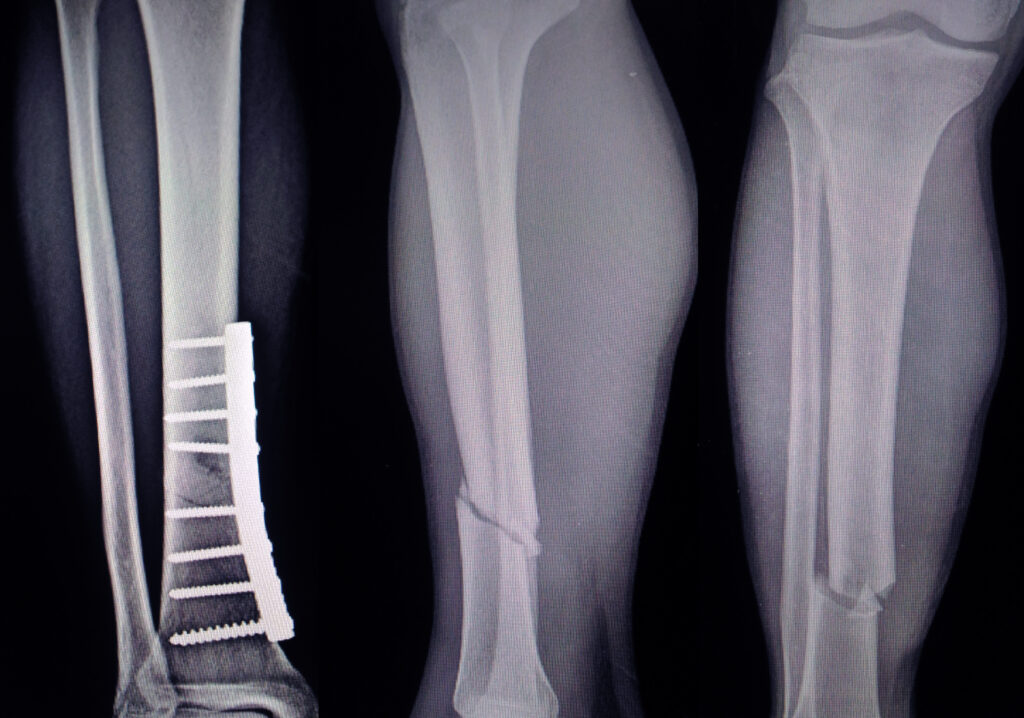
Knee fractures are serious injuries that involve a break in one or more of the bones that make up the knee joint. These bones include the patella (kneecap), the distal end of the femur (thighbone), and the proximal end of the tibia (shinbone). Knee fractures can result from high-impact trauma, such as falls, car accidents, or sports injuries, and they may significantly affect mobility and joint stability. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to restore knee function and prevent complications.
What Are Knee Fractures?
Knee fractures occur when one or more bones in the knee joint break due to trauma or underlying conditions that weaken the bone. The types of knee fractures include:
- Patellar Fractures: Breaks in the kneecap, which can affect the ability to straighten the leg.
- Distal Femur Fractures: Breaks in the lower end of the thighbone, which may extend into the knee joint.
- Proximal Tibia Fractures: Breaks in the upper end of the shinbone, often involving the tibial plateau, which is critical for weight-bearing and joint alignment.
Fractures may be classified as simple (clean breaks) or complex (involving multiple fragments or joint damage).
Causes Of Knee Fractures
Knee fractures are typically caused by high-energy trauma or excessive stress on the bone. Common causes include:
- Falls: Direct impact to the knee during a fall.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: High-impact collisions can result in severe fractures.
- Sports Injuries: High-intensity sports or activities involving sudden twists or impacts.
- Osteoporosis: Weak or brittle bones due to reduced bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
Symptoms Of Knee Fractures
Symptoms of knee fractures may vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the knee, especially when moving or bearing weight.
- Swelling and bruising around the knee joint.
- Inability to straighten or bend the knee fully.
- Deformity or misalignment of the knee.
- Difficulty walking or an inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Crepitus (grinding or crunching sensation) in the knee.
If you experience any of these symptoms following trauma, seeking immediate medical attention is essential.
Risk Factors For Knee Fractures
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of sustaining a knee fracture, including:
- High-Impact Activities: Sports or occupations that involve high levels of physical stress or risk of falls.
- Age: Older adults are more prone to fractures due to bone density loss.
- Osteoporosis: Reduced bone strength and density increase the risk of fractures.
- Previous Knee Injuries: A history of trauma or fractures in the knee area.
- Medical Conditions: Disorders that affect bone health, such as metabolic bone diseases.

Treatment Options For Knee Fractures
Treatment for knee fractures depends on the location, type, and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and activity level. Options include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Immobilisation: Using a brace or cast to stabilise the knee while the bone heals.
- Pain Management: Medications to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: Once the bone has healed, exercises may be recommended to restore strength, range of motion, and joint stability.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be required for complex fractures or those involving joint misalignment:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): Realigning the bone fragments and securing them with screws, plates, or rods.
- External Fixation: Using an external frame to stabilise the bone if internal fixation is not suitable.
- Bone Grafting: Using a graft to fill gaps or support the healing process in severe fractures.
- Knee Replacement Surgery: In cases of severe joint damage or arthritis following a fracture, partial or total knee replacement may be considered.
Dr. Scott Tulloch will assess your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment to promote healing and restore knee function.
When Should You Seek Help For Knee Fractures?
You should seek immediate medical attention if:
- You experience severe pain, swelling, or deformity in the knee after trauma.
- You are unable to move or bear weight on the affected leg.
- There is visible misalignment or an open wound over the knee.
Early intervention is critical for achieving the best possible outcome and minimising the risk of complications such as arthritis or chronic knee instability.
If you would like to learn more about knee fractures or discuss your treatment options, book an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group.
