MCL, LCL, PCL, And Complex Ligament Injuries
MCL, LCL, PCL, and Complex Ligament Injuries: Damage to Knee Stability and Function
The knee joint relies on several ligaments for stability and function, including the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). Injuries to these ligaments can result in pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty with knee movement. Complex ligament injuries, which involve damage to two or more ligaments, can significantly impact knee function and may require specialised treatment to restore stability and mobility.
- WHAT ARE MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES?
- CAUSES OF MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
- SYMPTOMS OF MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
- RISK FACTORS FOR KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES
- TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
- WHEN SHOULD YOU SEEK HELP FOR LIGAMENT INJURIES?
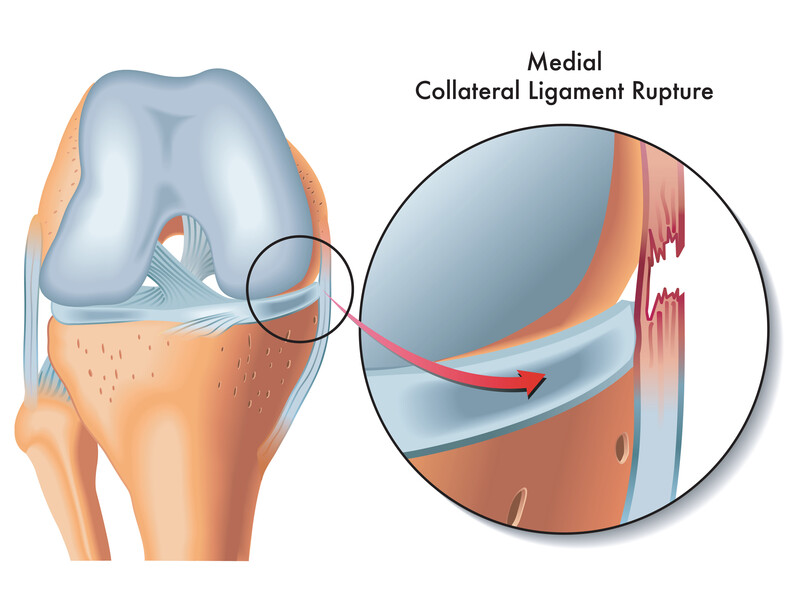
WHAT ARE MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES?
- MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament): The MCL is located on the inner side of the knee and provides stability against forces that push the knee inward. MCL injuries are often caused by direct blows to the outside of the knee.
- LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament): The LCL is located on the outer side of the knee and provides stability against forces that push the knee outward. LCL injuries are less common and often occur due to direct trauma or hyperextension.
- PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament): The PCL is located at the back of the knee and prevents the shinbone from moving backward relative to the thighbone. PCL injuries are often caused by high-impact trauma, such as car accidents or falls.
- Complex Ligament Injuries: These involve damage to two or more ligaments, often resulting from high-energy trauma such as sports injuries or motor vehicle accidents. Complex injuries may also affect other knee structures, such as cartilage or menisci.
CAUSES OF MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
These injuries can occur due to:
- Sports Injuries: Sudden changes in direction, twisting motions, or collisions in sports such as football, rugby, or skiing.
- Direct Trauma: Blows to the knee, often experienced in contact sports or motor vehicle accidents.
- Hyperextension: Overstretching the knee joint, causing ligament damage.
- Falls: High-impact falls that place excessive stress on the knee ligaments.
SYMPTOMS OF MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
Symptoms of ligament injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the ligaments involved. Common symptoms include:
- Pain at the site of the injury.
- Swelling and bruising around the knee.
- Instability or a feeling that the knee may “give way.”
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg.
- Limited range of motion or stiffness in the knee.
- A popping sound or sensation at the time of injury.
If left untreated, complex ligament injuries may lead to chronic instability, increased risk of further knee damage, and long-term joint issues.
RISK FACTORS FOR KNEE LIGAMENT INJURIES
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of ligament injuries, including:
- Sports Participation: High-risk sports involving sudden movements or contact.
- Previous Injuries: A history of knee injuries can increase susceptibility to reinjury.
- Poor Conditioning: Weak muscles around the knee joint may place additional strain on ligaments.
- Gender: Women may have a higher risk of certain ligament injuries due to anatomical and hormonal differences.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR MCL, LCL, PCL, AND COMPLEX LIGAMENT INJURIES
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury, the ligaments involved, and the patient’s activity goals. Options include:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE): To reduce pain and swelling in the initial phase.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening and stabilising the knee through a tailored rehabilitation program.
- Bracing: Knee braces may provide additional support and protection during healing.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that stress the knee joint while it heals.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be recommended for severe or complex injuries:
- Ligament Reconstruction: Replacing the damaged ligament with a graft to restore stability.
- Multiligament Reconstruction: Reconstructing multiple ligaments in a single surgery for complex injuries.
- Cartilage or Meniscal Repair: If additional structures are damaged, they may also require surgical repair.
Dr. Scott Tulloch will work with you to determine the most appropriate treatment based on your individual needs and injury severity.
When Should You Seek Help For Ligament Injuries?
You should consider seeking medical advice if:
- You experience knee pain, swelling, or instability after an injury.
- Your knee feels like it may “give way” during movement.
- You have difficulty bearing weight or fully extending your knee.
Early assessment and intervention may help reduce the risk of further damage and improve long-term outcomes.
If you would like to learn more about MCL, LCL, PCL, and complex ligament injuries or discuss your options, book an appointment with Dr. Scott Tulloch at the Victorian Orthopaedic Group.
